Last Updated on October 22, 2022
Introduction
• Pneumothorax = presence of air in pleural space
Classification
• Closed pneumothorax
• Open pneumothorax
• Tension pneumothorax
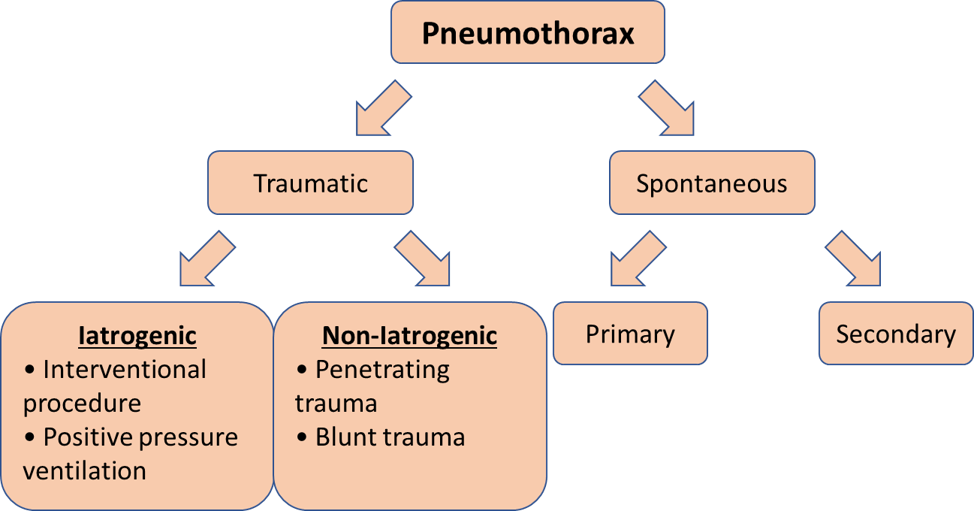
Traumatic pneumothorax
Examples of interventional procedures that cause pneumothorax
• Intercostal nerve block
• Chest aspiration
• Trachiobronchial biopsy
• Needle aspiration
• Lung biopsy
Secondary pneumothorax
Causes:
• COPD
• Asthma
• Tuberculosis
• Pleural malignancy
• Marfan’s syndrome
• Bacterial pneumonia
• Rheumatoid lung disease
Presentation
• Chest pain
• May have SOB
Clinical Features
Physical examination
(i) Lungs
• Reduced chest movement on the affected side
• Hyper-resonance of affected side
• Decreased breath sounds of affected side
(ii) Other findings
• Neck vein distension
• Subcutaneous emphysema of the chest wall / neck
• Trachea deviated away from affected side
• Hypotension
Management
• High flow-mask
Management of open pneumothorax
Temporary measure:
• Application of three-way occlusive dressing to the wound [Video]
Followed by:
• Chest tube insertion
Management of tension pneumothorax
• Chest tube insertion
=====
💡Notes
• If chest tube can be inserted immediately, no need to perform chest needle decompression prior to chest chest tube insertion
• Needle decompression for adult can be performed at safety triangle; needle decompression for paeds should be at 2nd intercostal space in the mid-clavicular line
Management of spontaneous pneumothorax
• Figure 2: Flowchart of management of spontaneous pneumothorax by British Thoracic Society
Points towards secondary spontaneous pneumothorax
• Age ≥50
• Smoking
• Evidence of underlying lung disease on exam / imaging
Primary pneumothorax with
Chest tube removal
Indications
- Lung is fully expanded
- No evidence of ongoing air leak
Preparation for chest tube removal
- Chest tube may be clamped for few hours prior to removal
- Observe for evidence of pneumothorax
- If pneumothorax recurs, chest drain can be unclamped, and chest drain cannot be removed first
Further reading
Related Posts
Q&A
Take Home Message
1. (Tension) Pneumothorax is a potentially fatal medical emergency without immediate treatment
2. (Tension) Pneumothorax is a clinical diagnosis. Do not wait until CXR available, which would delay treatment